Oral administration of the β-glucan produced by Aureobasidium pullulans ameliorates development of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E deficient mice
Highlights
•Aureobasidium pullulans-derived β-glucan (AP-PG) is known to be an immunomodulator.
•Apolipoprotein E deficient (ApoE) mice spontaneously develop atherosclerosis.
•AP-PG is effective in ameliorating development of atherosclerosis in the model mice.
•AP-PG administration reduces oxidized low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
Abstract
Abbreviations
ApoE
AP-PG
CAD
HDL
HFD
LDL
ox-LDL
Keywords
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Preparation of A. pullulans-derived β-glucan
2.3. Measurement of cholesterols and triacylglycerol
2.4. Histochemical and immunohistochemical analyses
2.5. Image analysis and statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Oral administration of AP-PG is effective to ameliorate development of atherosclerosis in ApoE deficient mice

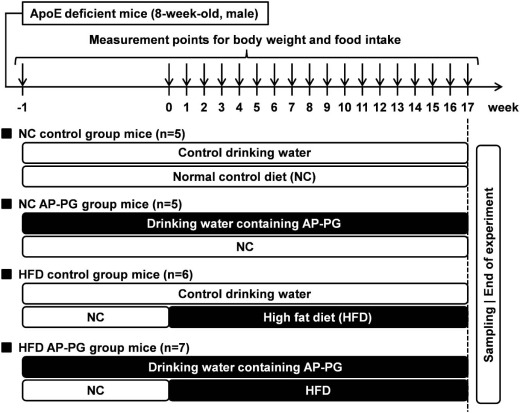
Fig. 1. Experimental design of this study.

Fig. 2. Oral administration of AP-PG effectively prevented high-fat diet-induced development of atherosclerotic plaque in ApoE deficient mice. (A and B) At the end of the period of the experiment, the main artery was isolated from the mice and atherosclerotic plaque formation was evaluated using Oil-O-Red staining. Data represent the image analysis results (A) and histopathological specimen images (B). Scale bars indicate 1 cm. (C) Image analysis of the atherosclerotic lesions on the aortic root sections. (D) Microphotographs of the histology of the aortic root sections stained with Oil-O-Red. Scale bars indicate 50 µm. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. NC: normal control diet. HFD: high-fat diet. n.s.: not significant.
3.2. Oral administration of AP-PG reduces blood levels of oxidized low-density lipoprotein cholesterol

Fig. 3. Evaluation of the effects of orally administered AP-PG on blood cholesterol levels (A–E). At the end of the period of the experiment, plasma levels of total cholesterol (A), triacylglycerol (B), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (C), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (D), and oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) cholesterol (E) in the mice were measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. NC: normal control diet. HFD: high-fat diet. n.s.: not significant.
3.3. Macrophage accumulation in vascular walls is reduced by oral administration of AP-PG
4. Discussion

Fig. 4. Oral administration of AP-PG is effective to prevent vascular accumulation of macrophages. (A and B) Sections of aortic roots sampled from the mice were immunostained with MOMA-2. (A) Percentages of MOMA-2 positive areas were calculated by image analysis. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. NC: normal control diet. HFD: high-fat diet. n.s.: not significant. (B) Microphotographs of immunohistology sections. Scale bars indicate 300 µm.